| Identification Number
Locations |
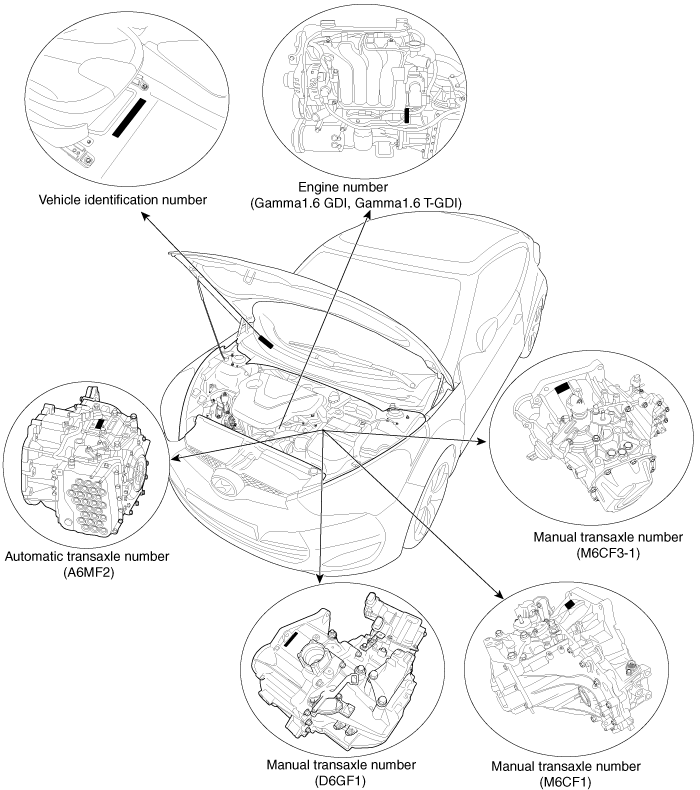
Identification Number Description
Vehicle Identification Number
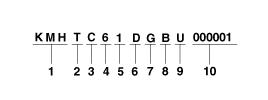
| 1. |
World Manufacturer Identifier
(WMI)
| A. |
KMF : Commercial vehicle
(Van) |
| B. |
KMH : Passenger vehicle or
MPV(Multipurpose Passenger Vehicle)/SUV(Sports Utility
Vehicle)/RV(Recreational
Vehicle) |
| D. |
KM8 : MPV/SUV/RV (For U.S.A, Canada,
Mexico
only) | |
| 3. |
Model & Series
| B. |
B : Middle-Low grade
(GL) |
| C. |
C : Middle grade (GLS, JSL,
TAX) |
| D. |
D : Middle-High grade
(HGS) |
|
| 4. |
Body/Cabin type, Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating
KMF (Commercial vehicle / Van)
Except U.S.A, Canada, Mexico, Gulf Cooperation
Council, China
- X : Standard Cabin /
Semi-Bonnet
- Y : Double Cabin / Bonnet
- Z : Super Cabin / Box
For U.S.A, Canada, Mexico, Gulf Cooperation
Council, China
- 3 : Standard Cabin Class-E 4×2 / Semi-Bonnet
Class-E 4×2
- 4 : Standard Cabin Class-E 4×4 / Semi-Bonnet
Class-E 4×4
- 5 : Standard Cabin Class-F 4×2 / Semi-Bonnet
Class-F 4×2
- 6 : Standard Cabin Class-F 4×4 / Semi-Bonnet
Class-F 4×4
- 7 : Double Cabin Class-E 4×2 / Bonnet
Class-E 4×2
- 8 : Double Cabin Class-E 4×4 / Bonnet
Class-E 4×4
- 9 : Double Cabin Class-F 4×2 / Bonnet
Class-F 4×2
- 0 : Double Cabin Class-F 4×4 / Bonnet
Class-F 4×4
- A : Super Cabin Class-E 4×2 / Box Class-E
4×2
- B : Super Cabin Class-E 4×4 / Box Class-E
4×4
- C : Super Cabin Class-F 4×2 / Box Class-F
4×2
- D : Super Cabin Class-F 4×4 / Box Class-F
4×4
KMH
- 1 : Limousine
- 2 : Sedan - 2 door
- 3 : Sedan - 3 door
- 4 : Sedan - 4 door
- 5 : Sedan - 5 door
- 6 : Coupe
- 7 : Convertible
- 8 : Wagon
- 9 : Commercial Van
- 0 : Pick-Up
KMJ
- 1 : Box
- 2 : Bonnet
- 3 : Semi-Bonnet
KM8
- 1 : Wagon 4×2 Class-A
- 2 : Wagon 4×2 Class-B
- 3 : Wagon 4×2 Class-C
- 4 : Wagon 4×2 Class-D
- 5 : Wagon 4×2 Class-E
- 6 : Wagon 4×2 Class-F
- 7 : Wagon 4×2 Class-G
- A : Wagon 4×4 Class-A
- B : Wagon 4×4 Class-B
- C : Wagon 4×4 Class-C
- D : Wagon 4×4 Class-D
- E : Wagon 4×4 Class-E
- F : Wagon 4×4 Class-F
- G : Wagon 4×4
Class-G |
| 5. |
Restraint system, Brake system
KMH, KM8
Except U.S.A, Canada, Mexico
- 0 : Both side - None
- 1 : Both side - Active belt
- 2 : Both side - Passive belt
For U.S.A, Canada, Mexico
Code
|
Seat belt
|
Front air bag
|
Knee air bag
|
Side air bag
|
Curtain air bag
|
Driver's
|
Passenger's
|
Driver's
|
Passenger's
|
1st
row
|
2nd
row
|
3rd
row
|
1st
row
|
2nd
row
|
3rd
row
|
A
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
B
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
C
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
D
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
E
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
F
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
J
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
L
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
N
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
KMJ
Except U.S.A, Canada, Mexico
- 7 : Hydraulic brake system
- 8 : Pneumatic brake system
- 9 : Mixed brake system
For U.S.A, Canada, Mexico
- X : Hydraulic brake system
- Y : Pneumatic brake system
- Z : Mixed brake system
KMF
Except U.S.A, Canada, Mexico
- 7 : Hydraulic brake system
- 8 : Pneumatic brake system
- 9 : Mixed brake system
For U.S.A, Canada, Mexico
Code
|
Restraint system
|
Brake system
|
Seat belt
|
Front air bag
|
Knee air bag
|
Side air bag
|
Curtain air bag
|
Hydraulic
|
Pneumatic
|
Mixed
|
Driver's
|
Passenger's
|
Driver's
|
Passenger's
|
1st
row
|
2nd
row
|
3rd
row
|
1st
row
|
2nd
row
|
3rd
row
|
X
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
-
|
-
|
V
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
-
|
-
|
W
|
○
|
○
|
○
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
×
|
○
|
-
|
-
|
|
| 6. |
Engine type
| A. |
D : Gasoline engine 1.6 (Gamma
GDI) |
| B. |
E : Gasoline engine 1.6 (Gamma
T-GDI) | |
| 7. |
Check digit or Driver’s side &
Transmission
Except U.S.A, Canada, Mexico, Gulf Cooperation
Council, China, Yemen
- A : LHD & MT
- B : LHD & AT
- C : LHD & MT+Transfer
- D : LHD & AT+Transfer
- E : LHD & CVT
- F : LHD & Decelerator
- G : LHD & DCT
- L : RHD & MT
- M : RHD & AT
- N : RHD & MT+Transfer
- S : RHD & AT+Transfer
- T : RHD & CVT
- U : RHD & Decelerator
- V : RHD & DCT
For U.S.A, Canada, Mexico, Gulf Cooperation
Council, China, Yemen
- Check digit : 0 ~ 9,
× |
| 8. |
Model year
| A. |
B : 2011, C : 2012, D : 2013, E : 2014
... | |
| 10. |
Vehicle production sequence
number
|
Paint Code
Code
|
Color
|
MZH
|
Phantom
black
|
PGU
|
White
crystal
|
RHM
|
Sleek
silver
|
N9S
|
Sonic
silver
|
P9R
|
Veloster
red
|
R9A
|
Vitamin
C
|
SYY
|
Sun
flower
|
T9U
|
Clean
blue
|
UU9
|
Blue
ocean
|
VE9
|
Green
apple
|
Engine Number
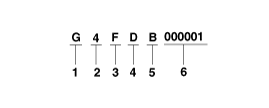
| 1. |
Engine fuel
- G :
Gasoline |
| 2. |
Engine range
- 4 : 4 cycle 4
cylinder |
| 3. |
Engine development order and
capacity
- F : Gamma engine
(Gasoline) |
| 4. |
Engine Capacity
- D : 1591cc (Gamma GDI engine)
- J : 1591cc (Gamma T-GDI
engine) |
| 5. |
Production year
- B : 2011, C : 2012, D : 2013, E : 2014
... |
| 6. |
Plant of production
- A : Asan (Korea)
- B : Beijing (China)
- H : Hwasung (Korea)
- K : Montgomery (U.S.A)
- M : Chennai (India)
- P : Poseung (Korea)
- S : Sohari (Korea)
- T : Izmit (Turkey)
- U : Ulsan (Korea)
- W : Shandong (China)
- Z : Zilina (Slovakia)
- 1 : Yancheng
(China) |
| 7. |
Engine production sequence number
- 000001 ~
999999 |
Transaxle Number
Manual (M6CF1)
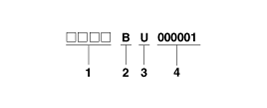
| 1. |
Assembly code of
plant |
| 2. |
Production year
- B : 2011, C : 2012, D : 2013, E : 2014
... |
| 3. |
Plant of production
- U : Ulsan (Korea)
- J : Ostrava
(Czech) |
| 4. |
Transaxle production sequence
number
- 000001 ~
999999 |
Manual (M6CF3-1)
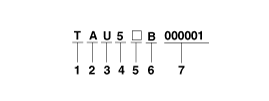
| 2. |
Production year
- B : 2011, C : 2012, D : 2013, E : 2014
... |
| 3. |
Plant of production
- U : Ulsan
(Korea) |
| 4. |
Shift position
- 6 : 6th |
| 6. |
Final gear ratio
- L : 4.467 |
| 7. |
Transaxle production sequence
number
- 000001 ~
999999 |
Manual (D6GF1)
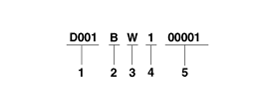
| 1. |
Assembly code
- D001 :
D6GF1 |
| 2. |
Production year
- B : 2011, C : 2012, D : 2013, E : 2014
... |
| 3. |
Plant of production
- W : Hyundai -
WIA |
| 5. |
Transaxle production sequence
number
- 000001 ~
999999 |
Automatic
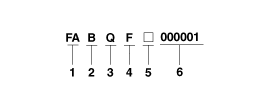
| 2. |
Production year
- B : 2011, C : 2012, D : 2013, E : 2014
.. |
| 3. |
Gear ratio
- Q : 3.270 (A6GF1)
- R : 3.612
- H : 3.648
(A6MF2) |
| 4. |
Detailed classification
- F : Gamma 1.6 GDI
- G : Gamma 1.6 GDI ISG
- D : Gamma 1.6 MPI
- A : Gamma 1.6
T-GDI |
| 6. |
Transaxle production sequence
number
- 000001 ~
999999 |
Warning / Caution Label Locations
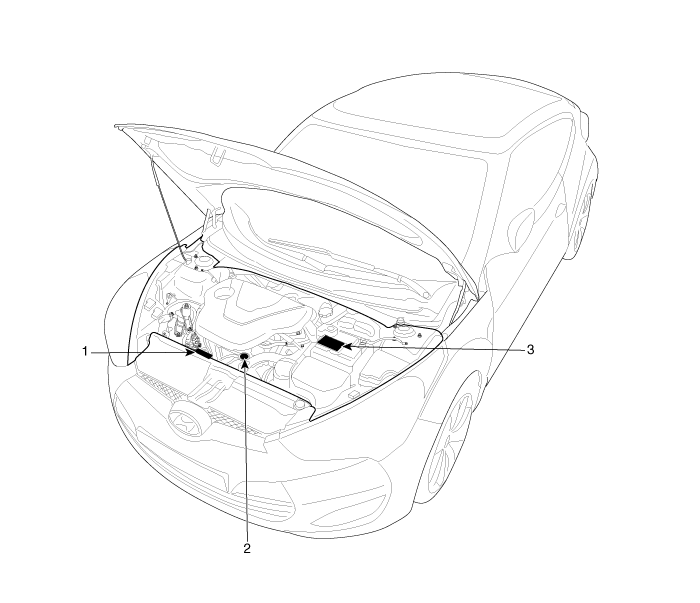
1. Fan
caution
2. Radiator cap
caution
|
3. Battery
caution
|
Battery Caution Label Description
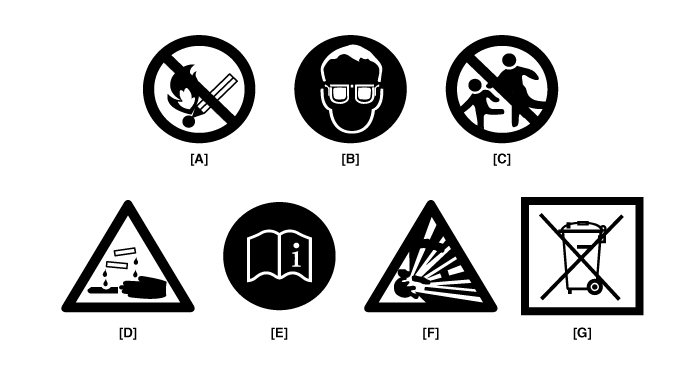
Warning / Caution Label
(Cont'd)
A.
Keep lighted cigarettes and
all other flames or sparks away from the
battery.
|
B.
Wear eye protection when
charging or working near a battery. Always provide ventilation when
working in an enclosed space.
| •
|
When lifting a plastic-cased battery,
excessive pressure on acid to leak resulting in personal
injury. Lift with a battery carrier or with your hands on
opposite corners. |
| •
|
Never attempt to change the battery when
the battery cables are
connected. |
| •
|
The electrical ignition system works
with high voltage.
Never touch these components with the
engine running or the ignition switched
on. | |
C.
Keep batteries out of the
reach of children because batteries contain highly corrosive
SULFURIC ACID. Do not allow battery acid to contact your skin, eyes,
clothing or paint finish.
|
D.
If any electrolyte gets
into your eyes, flush your eyes with clean water for at least 15
minutes and get immediate medical attention. If possible, continue
to apply water with a sponge or cloth until medical attention is
received.
If electrolyte gets on your
skin, throughly wash the contacted area. If you feel a pain or a
burning sensation, get medical attention
immediately.
|
E.
Always read the following
instructions carefully when handing a
battery.
|
F.
Hydrogen, which is a highly
combustible gas, is always presents in battery cells and may explode
if ignited.
|
G.
An improperly disposed
battery can be harmful to the environment and human
health.
Always confirm local regulations
for battery disposal.
|
Handling And Storage The
Battery
Battery
Itself
|
| •
|
Batteries should be stored in cool, dry
(27 degrees Celsius) places and out of direct
sunlight. |
| •
|
MF batteries are tightly sealed to
prevent acid leakage.
However, tilting the battery to an angle
of 45 degrees can cause acid to leak through the vents on the
sides. Therefore, batteries should always be stored in their
upright positions. Prevent placing any aqueous or solid (i.e.
conductors) bodies on top of the
battery. |
| •
|
It is extremely dangerous to use tools,
such as hammers, on the battery terminals when connecting
cables to the mounted
battery. | |
Battery on
Vehicle
|
| •
|
When storing the vehicle for long
periods of time, make sure to remove the memory fuse at
junction box to prevent natural
discharging. |
| •
|
Also, run the engine for battery
charging within 1 month if the memory fuse wasn't removed from
the start of vehicle storing.
If the memory fuse was removed, run the
engine for battery charging within 3 months from the start of
vehicle
storing. | |
|
After reconnecting or recharging a discharged
battery, the ESP OFF indicator may illuminate.
In this case, turn the handle half way to the
left and right whilst the ignition switch is in the ON
position.
Then, restart the engine after the ignition is
OFF.
The ESP OFF indicator may turn
OFF.
If the ESP OFF indicator does not turn OFF,
have the system checked reffering to DTC. (Refer to the BR
group.) |
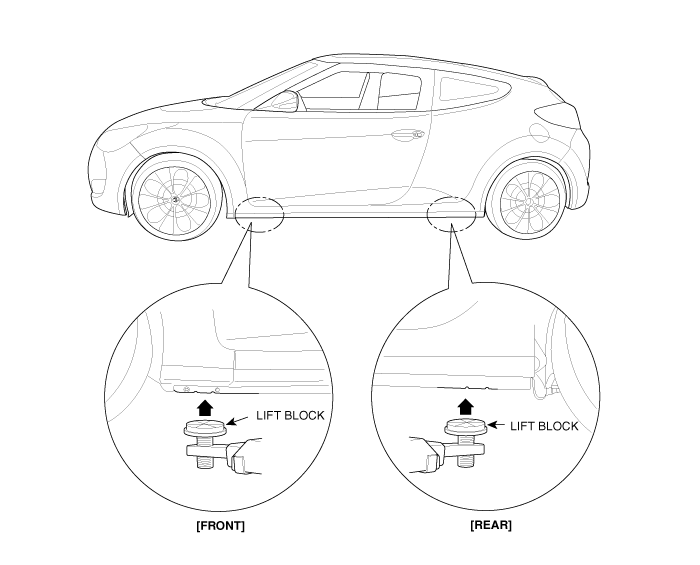
Lift And Support Points
|
When heavy rear components such as suspension,
fuel tank, spare tire, tailgate and trunk lid are to be removed,
place additional weight in the luggage area before hoisting. When
substantial weight is removed from the rear of the vehicle, the
center of gravity may change and can cause the vehicle to tip
forward on the hoist. |
| •
|
Since each tire/wheel assembly weights
approximately 30lbs (14kg), placing the front wheels in the
luggage area can assist with the weight
distribution. |
| •
|
Use the same support points to support
the vehicle on safety
stands. | |
| 1. |
Place the lift blocks under the support points
as shown in the illustration. |
| 2. |
Raise the hoist a few inches (centimeters) and
rock the vehicle to be sure it is firmly
supported. |
| 3. |
Raise the hoist to full height to inspect the
lift points for secure support. |
Towing
If the vehicle needs to
be towed, call a professional towing service. Never tow vehicle with just
a rope or chain. It is very dangerous.
Emergency Towing
There are three popular
methods of towing a vehicle :
| - |
The operator loads the vehicle on the back of
truck. This is best way of transporting the vehicle.
|
| - |
The tow truck uses two pivoting arms that go
under the tires of the driving axle and lift them off the ground.
The other two wheels remain on the ground.
|
| - |
The tow truck uses metal cables with hooks on
the ends. These hooks go around parts of the frame or suspension,
and the cables lift that end of the vehicle off the ground. The
vehicle's suspension and body can be seriously damaged if this
method of towing is attempted. |
If the vehicle cannot be
transported by flat-bed, should be towed with the wheels of the driving
axle off the ground and do the following :
Manual Transaxle
| • |
Release the parking brake.
|
| • |
Shift the Transaxle to neutral
|
Automatic Transaxle
| • |
Release the parking brake.
|
| • |
Shift to [D] position, then [N] position.
|
| •
|
The vehicle equipped with full-time 4WD
should be only transported on a
flat-bed. |
| •
|
Improper towing preparation will damage
the transaxle. follow the above procedure exactly. If you
cannot shift the transaxle or start the engine(automatic
transaxle), your vehicle must be transported on a
flatbed. |
| •
|
It is the best to tow vehicle no farther
than 30km (19miles), and keep the speed below 50km/h (30mph).
(For the full-time 4WD vehicle, limit the towing to 1.5km
(1mile) and 15km/h (10mph) |
| •
|
Trying to lift or tow your vehicle by
the bumpers will cause serious damage. The bumpers are not
designed to support the vehicle's
weight. | |
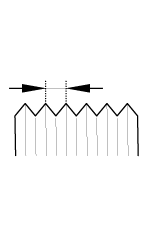
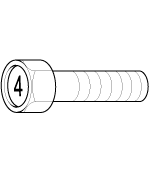
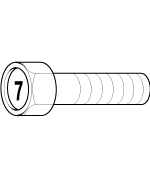
Tightening Torque Table Of Standard
Parts
Bolt nominal
diameter (mm)
|
Pitch (mm)
|
Torque Nm (kg.cm,
lb.ft)
|
Head Mark 4
|
Head Mark 7
|
|
|
|
|
|
M5
|
0.8
|
3 ~ 4 (30 ~ 40,
2.2 ~ 2.9)
|
5 ~ 6 (50 ~ 60,
3.6 ~ 4.3)
|
M6
|
1.0
|
5 ~ 6 (50 ~ 50,
3.6 ~ 4.3)
|
9 ~ 11 (90 ~
110, 6.5 ~ 8.0)
|
M8
|
1.25
|
12 ~ 15 (120 ~
150, 9 ~ 11)
|
20 ~ 25 (200 ~
250, 14.5 ~ 18.0 )
|
M10
|
1.25
|
25 ~ 30 (250 ~
300, 18 ~ 22)
|
30 ~ 50 (300 ~
500, 22 ~ 36)
|
M12
|
1.25
|
35 ~ 45 (350 ~
450, 25 ~ 33)
|
60 ~ 80 (600 ~
800, 43 ~ 58)
|
M14
|
1.5
|
75 ~ 85 (750 ~
850, 54 ~ 61)
|
120 ~ 140
(1,200 ~ 1,400, 85 ~ 100)
|
M16
|
1.5
|
110 ~ 130
(1,100 ~ 1,300, 80 ~ 94)
|
180 ~ 210
(1,800 ~ 2,100, 130 ~ 150)
|
M18
|
1.5
|
160 ~ 180
(1,600 ~ 1,800, 116 ~ 130)
|
260 ~ 300
(2,600 ~ 3,000, 190 ~ 215)
|
M20
|
1.5
|
220 ~ 250
(2,200 ~ 2,500, 160 ~ 180)
|
360 ~ 420
(3,600 ~ 4,200, 260 ~ 300)
|
M22
|
1.5
|
290 ~ 330
(2,900 ~ 3,300, 210 ~ 240)
|
480 ~ 550
(4,800 ~ 5,500, 350 ~ 400)
|
M24
|
1.5
|
360 ~ 420
(3,600 ~ 4,200, 260 ~ 300)
|
610 ~ 700
(6,100 ~ 7,000, 440 ~ 505)
|
| 1. |
The torques shown in the table are
standard values under the following
conditions. |
| •
|
Nuts and bolts are made of
galvanized steel bar. |
| •
|
Galvanized plain steel washers are
inserted. |
| •
|
All nuts, bolts and plain washers
are
dry. | |
| 2. |
The torques shown in the table are not
applicable. |
| •
|
When spring washers, toothed
washers and the like are
inserted. |
| •
|
If plastic parts are
fastened. |
| •
|
If self-tapping screws or
self-locking nuts are
used. |
| •
|
If threads and surfaces are coated
with
oil. | |
| 3. |
Reduce the torque values to the
indicated percentage of the standard value under the following
conditions. |
| •
|
If spring washers are used :
85% |
| •
|
If threads and bearing surfaces
are stained with oil :
85% | | |
Meaning Of Symbols
There are five primary
symbols used to complement illustrations. These symbols indicate the part
to apply such materials during service.
Symbol
|
Meaning
|
|

|
Do not reuse
the part. Replace a new one.
|
|

|
Apply engine
oil or transmission oil to the part.
|
|

|
Apply
automatic transmission fluid (ATF) to the part.
|
|

|
Apply grease
to the part.
|
|

|
Apply sealant
to the part.
|
General Service Information
Protection Of The Vehicle
Always be sure to cover
fenders, seats, and floor areas before starting work.
|
The support rod must be inserted into the hole
near the edge of the hood whenever you inspect the engine
compartment to prevent the hood from falling and causing possible
injury.
Make sure that the support rod has been
released prior to closing the hood. Always check to be sure the hood
is firmly latched before driving the
vehicle. |
Preparation Of Tools And Measuring
Equipment
Be sure that all
necessary tools and measuring equipment are available starting
work.
Special Tools
Use special tools when
they are required.
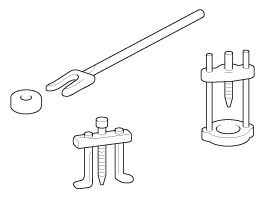
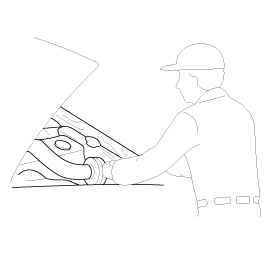
Removal Of Parts
First find the cause of
the problem and then determine whether removal or disassembly before
starting the job.
Disassembly
If the disassembly
procedure is complex, requiring many parts to be disassembled, all parts
should be disassembled in a way that will not affect their performance or
external appearance.
| 1. |
Inspection of
parts
Each part, when removed, should be carefully
on suspected for malfunction, deformation, damage, and other
problems.
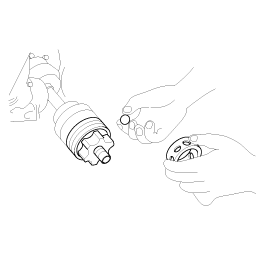
|
| 2. |
Arrangement of
parts
All disassembled parts should be carefully
arranged for effective reassembly.
Be sure to separate and correctly identify the
parts to be replaced from those that will be used
again.
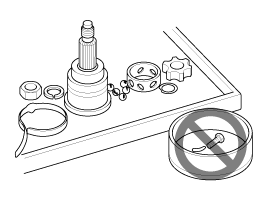
|
| 3. |
Cleaning parts for
reuse
All parts to be used again should be carefully
and thoroughly cleaned by an appropriate method.
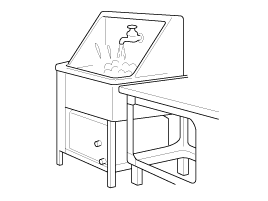
|
Parts
When replacing parts,
use HYUNDAI genuine parts.
Replacement
Standard values, such as
torques and certain adjustments, must be strictly observed in the
reassembly of all parts.
If removed, the
following parts should always be replaced with new ones.
| 5. |
Cotter pins (split
pins) |
| 6. |
Plastic nuts
Depending on their
location. |
| 7. |
Sealant should be applied to
gaskets. |
| 8. |
Oil should be applied to the moving components
of parts. |
| 9. |
Specified oil or grease should be applied to
the prescribed locations (oil seals, etc) before
assembly.
|
Adjustment
Use gauges and testers
to adjust correctly the parts to standard values correctly.
Electrical System
| 1. |
Be sure to disconnect the battery cable from
the negative (-) terminal of the
battery. |
| 2. |
Never pull on the wires when disconnecting
connectors. |
| 3. |
Locking connectors will click when the
connector is secure. |
| 4. |
Handle sensors and relays carefully. Be
careful not to drop them against other parts.
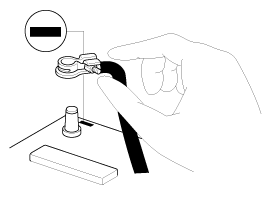
|
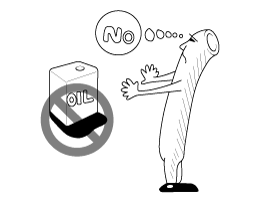
Rubber Parts And Tubes
Always prevent gasoline
or from touching rubber parts or tubing.
Measuring Body Dimensions
| 1. |
Basically, all measurements in this manual are
taken with a tracking gauge. |
| 2. |
When a measuring tape is used, check to be
sure there is no elongation, twisting or
bending. |
| 3. |
For measuring dimensions, both projected
dimensions and actual - measurement dimensions are used in this
manual. |
Dimensions Projected
| 1. |
These are the dimensions measured when the
measurement points are projected from the vehicle's surface, and are
the reference dimensions used for used for body
alterations. |
| 2. |
If the length of the tracking gauge probes is
adjustable, measure it by lengthening one of two probes as long as
the different value in height of the two surface.
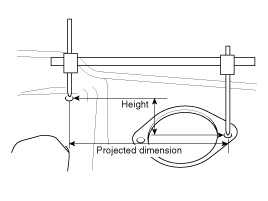
|
Measuring Actual Dimensions
| 1. |
These dimensions indicate the actual linear
distance between measurement points, and are used as the reference
dimensions when a tracking gauge is used for
measurement. |
| 2. |
First adjust both probes to the same length
(A=A') before measurement.
|
Check the probes and gauge itself to
make sure there is no free
play. |
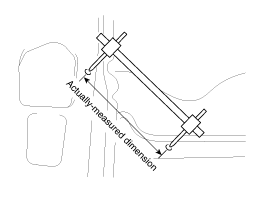
|
Measurement Point
Measurements should be
taken at the center of the hole.
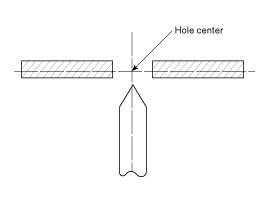
Checking Cables And Wires
| 1. |
Check the terminal for
tightness. |
| 2. |
Check terminals and wires for corrosion from
battery electrolyte, etc. |
| 3. |
Check terminals and wires for open
circuits. |
| 4. |
Check wire insulation and coating for damage,
cracks and degrading. |
| 5. |
Check the conductive parts of terminals for
contact with other metallic parts (vehicle body and other
parts). |
| 6. |
Check grounded parts to verify that there is
complete continuity between their attaching bolt(s) and the
vehicle's body. |
| 7. |
Check for incorrect
wiring. |
| 8. |
Check that the wiring is so clamped to the
prevent contact with sharp corners of the vehicle body, etc. or hot
parts (exhaust manifold, etc.) |
| 9. |
Check that the wiring is clamped firmly to
provide enough clearance from the fan pulley, fan belt and other
rotating or moving parts. |
| 10. |
Check that the wiring has a little space so
that it can vibrate between fixed and moving parts such as the
vehicle body and the engine.
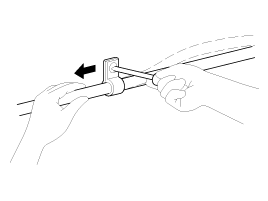
|
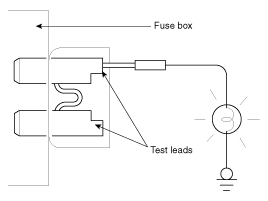
Check Fuses
A blade type fuse test
taps provided to allow checking the fuse itself without removing if from
the fuse box. The fuse is good if the test lamp lights up when one lead is
connected to the test taps (one at a time) and the other lead is grounded.
(Turn the ignition switch so that the fuse circuit becomes
operative)
Servicing The Electrical System
| 1. |
Prior to servicing the electrical system, be
sure to turn off the ignition switch and disconnect the battery
ground cable.
|
In the course of MFI or ELC system
diagnosis, when the battery cable is removed, any diagnostic
trouble code retained by the computer will be cleared. There
fore, if necessary, record the diagnostic data before removing
the battery cable. |
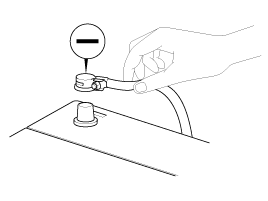
|
| 2. |
Attach the wiring harnesses with clamps so
that there is no slack. However, for any harness which passes the
engine or other vibrating parts of the vehicle, allow some slack
within a range that does not allow the engine vibrations to cause
the harness to come into contact with any of the surrounding parts
and then secure the harness by using a clamp.

|
| 3. |
If any section of a wiring harness interferes
with the edge of a parts, or a corner, wrap the section of the
harness with tape or something similar in order to protect if from
damage.
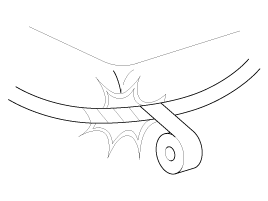
|
| 4. |
When installing any parts, be careful not to
pinch or damage any of the wiring harness.
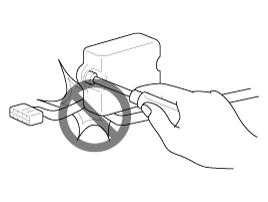
|
| 5. |
Never throw relays, sensors or electrical
parts, or expose them to strong shock.
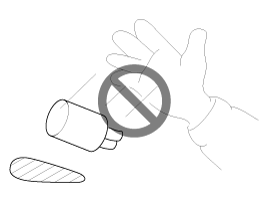
|
| 6. |
The electronic parts used in the computer,
relays, etc. are readily damaged by heat. If there is a need for
service operations that may cause the temperature to exceed 80°C
(176°F), remove the electronic parts before hand.
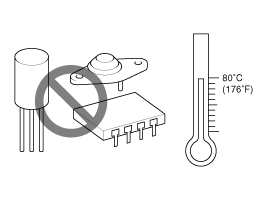
|
| 7. |
Loose connectors cause problems. Make sure
that the connectors are always securely fastened.
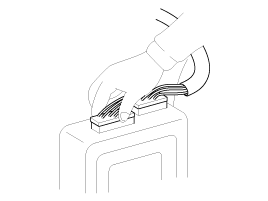
|
| 8. |
When disconnecting a connector, be sure to
grip only the connector, not the wires.
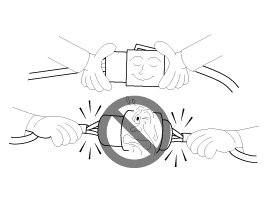
|
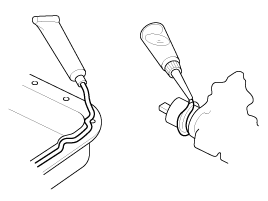
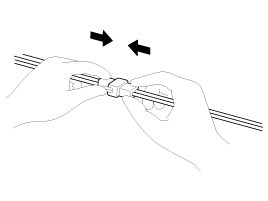
| 9. |
Disconnect connector which have catches by
pressing in the direction of the arrows shown the
illustration.
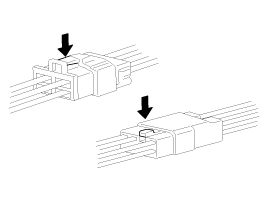
|
| 10. |
Connect connectors which have catches by
inserting the connectors until they make a clicking
sound.
|
| 11. |
When using a circuit tester to check
continuity or voltage on connector terminals, insert the test probe
into the harness side. If the connector is a sealed connector,
insert the test probe through the hole in the rubber cap until
contacts the terminal, being careful not to damage the insulation of
the wires.
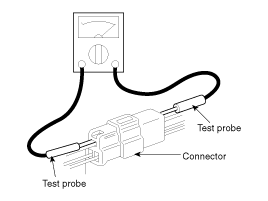
|
| 12. |
To avoid overloading the wiring, take the
electrical current load of the optional equipment into
consideration, and determine the appropriate wire size.
Nominal
size
|
SAE gauge
No.
|
Permissible
current
|
In engine
compartment
|
Other
areas
|
0.3mm²
|
AWG
22
|
-
|
5A
|
0.5mm²
|
AWG
20
|
7A
|
13A
|
0.85mm²
|
AWG
18
|
9A
|
17A
|
1.25mm²
|
AWG
16
|
12A
|
22A
|
2.0mm²
|
AWG
14
|
16A
|
30A
|
3.0mm²
|
AWG
12
|
21A
|
40A
|
5.0mm²
|
AWG
10
|
31A
|
54A
|
|
Precautions For Catalytic Converter
|
If a large amount of unburned gasoline flows
into the converter, it may overheat and create a fire hazard. To
prevent this observe the following precautions and explain them to
your customer. |
| 1. |
Use only unleaded
gasoline. |
| 2. |
Do not run the engine while the car is at rest
for a long time. Avoid running the engine at fast idle for more than
10minutes and idle speed for more than 20
minutes. |
| 3. |
Do not measure engine compression for an
extended time. Engine compression tests must be made as rapidly as
possible. Remove the fuel pump relay before performing a compression
test. |
| 4. |
Do not dispose of used catalytic converter
together with parts contaminated with gasoline or
oil. | |