| Turbocharger
Diagnostic Flow |
If any problem related with turbocharger, such as lack of
engine power, poor acceleration, abnormal engine noise or oil leaks, may
occur, check the turbocharger according to the procedure as
follows.
| 1. |
Check for assembling of the turbocharger and
the exhaust fitting (or the after treatment).
| A. |
Check if a gasket is
installed. |
| A. |
Check if mounting bolts (or nuts) are
tightened properly. |
| A. |
Check if there is a gas
leak. |
| A. |
Check if there is any damage, such as
crack, on the parts. |
If a gas leak occur as a gasket was not
installed or mounting bolts (or nuts) were tightened inadequately,
it may cause abnormal engine noise.
If the cause of the problem is detected,
retighten the mounting bolts (or nuts) as the specified torque or
replace the gasket or damaged parts with new ones if
necessary. |
| 2. |
Check for assembling of the turbocharger and
the exhaust manifold.
| A. |
Check if a gasket is
installed. |
| B. |
Check if the mounting bolts (or nuts)
are tightened properly. |
| C. |
Check if there is a gas
leak. |
| D. |
Check if there is any damage, such as
crack, on the parts. |
If a gas leak occur as a gasket was not
installed or mounting bolts (or nuts) were tightened inadequately,
it may cause abnormal engine noise.
If the cause of the problem is detected,
retighten the mounting bolts (or nuts) as the specified torque or
replace the gasket or damaged parts with new ones if
necessary. |
| 3. |
Check for assembling of the exhaust manifold
and the cylinder head.
| A. |
Check if a gasket is
installed. |
| B. |
Check if the mounting bolts (or nuts)
are tightened properly. |
| C. |
Check if there is a gas
leak. |
If a gas leak occur as a gasket was not
installed or mounting bolts (or nuts) were tightened inadequately,
it may cause abnormal engine noise.
If the cause of the problem is detected,
retighten the mounting bolts (or nuts) as the specified torque or
install a new gasket if necessary. |
| 4. |
Check the turbocharger oil feed pipe &
hose and oil drain pipe & hose.
| A. |
Check if a gasket is
installed. |
| B. |
Check if the mounting bolts are
tightened properly. |
| C. |
Check if the clamps are positioned in
place. |
| D. |
Check if the oil pipes & hoses are
damaged (bent, crushed, torn or
cracked). |
If a gas leak occur as a gasket was not
installed or mounting bolts were tightened inadequately, it may
cause oil leaks.
If the oil feed pipe & hose is damaged,
engine oil is not supplied sufficiently to the turbocharger then it
may damage the turbocharger. If the oil drain pipe & hose is
damaged and clogged, engine oil is not drained smoothly then it may
cause oil leaks from the turbocharger.
If the cause of the problem is detected,
retighten the mounting bolts (or nuts) as the specified torque or
replace the gasket or damaged parts with new ones if
necessary. |
| 5. |
Check for oil leaks between center housing and
compressor housing.
| A. |
Check if the mounting bolts are
tightened properly. |
| B. |
Check if there is an oil
leak. |
If the O-ring (gasket) between the center
housing and the compressor housing is damaged, it may cause oil
leaks.
If an oil leak is detected, replace the
turbocharger with a new one. |
| 6. |
Check the setting marks of the turbocharger
actuator rod.
| A. |
Check if the actuator rod setting mark
(A) is aligned in line.
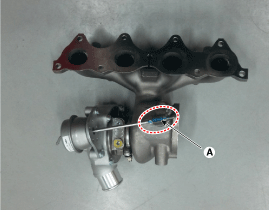
|
If the setting marks are not aligned in line,
the engine performance is changed by an arbitrary tune-up of the
turbocharger after delivery.
If the setting marks are not aligned in line,
replace the turbocharger with a new
one. |
| 7. |
Check the turbocharger actuator vacuum hoses
& pipes.
| A. |
Check if the vacuum hose is connected to
the actuator properly. |
| B. |
Check if the vacuum hoses & pipes
are damaged (bent, detached or
torn). |
| C. |
Check if there is any damage, such as
crack, on the vacuum pipes. |
| D. |
Check if the vacuum hoses are connected
to inlet or outlet of the solenoid valve
correctly. |
If the vacuum pipes & hoses are damaged or
disconnected, the actuator does not work properly then it may cause
lack of engine power and poor acceleration.
If the vacuum hoses & pipes are damaged,
replace them with new ones. |
| 8. |
Check the turbocharger actuator.
| A. |
Vacuum type actuator : Check for
movement of the actuator rod when a vacuum of 62.6kPa
(470mmHg, 9.08psi) is applied to the actuator.
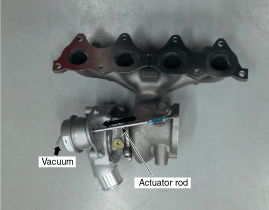
|
If the turbocharger actuator is damaged, it
may cause lack of engine power and poor acceleration.
If the actuator rod does not move, replace the
turbocharger with a new one. |
| 9. |
Check the turbocharger compressor
wheel.
| A. |
Check if the compressor wheel is damaged
(bent or deformed). |
| B. |
Check if the compressor wheel rotates
smoothly.
EX)
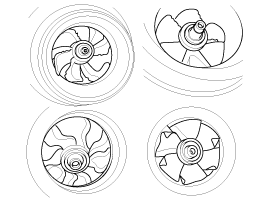
|
If the compressor wheel are damaged, it may
cause abnormal noise from the turbocharger and poor acceleration.
If the compressor wheel are damaged or
deformed, replace the turbocharger with new
ones. |
| 10. |
Check the turbocharger turbine
wheel.
| A. |
Check if the turbine wheel is
damaged. |
| B. |
Check if the turbine wheel rotates
smoothly.
EX)
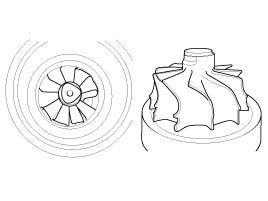
|
If the turbine wheel are damaged, it may cause
abnormal noise from the turbocharger and poor acceleration.
If the turbine wheel are damaged or deformed,
replace the turbocharger with new
ones. |
If any problem is not detected in the turbocharger, check the
turbocharger-related parts according to the procedure as
follows.
| 1. |
Check the blow-by hose.
| A. |
Check if the breather hose is damaged
(bent, clogged). |
| B. |
Check if the positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) valve is
clogged. |
If the breather hose is bent or clogged, the
internal pressure in the engine increases then engine oil is not
supplied smoothly to the turbocharger. So it may cause damage of the
turbocharger and oil leaks.
If the cause of the problem is detected,
replace the breather hose or the related parts with new
ones. |
| 2. |
Check the air intake hose connected to the
turbocharger.
| A. |
Check if the air intake hose is damaged
(bent, crushed, detached or
torn). |
If a cross-section of the hose diminishes as
the air intake hose is bent or crushed, intake air to the
turbocharger reduces and the pressure in front of turbocharger
drops. So it may cause damage of the turbocharger and oil leaks. If
the air intake hose is detached or torn, a foreign substance goes
into the turbocharger and causes damage of it.
If the air intake hose is damaged, replace it
with a new one. |
| 3. |
Check the air cleaner.
| A. |
Check the air cleaner filter for
pollution state. |
| B. |
Check the air cleaner filter for water
influx. |
| C. |
Check the air cleaner cover for
dirtiness. |
| D. |
Check if the air cleaner filter is a
genuine part.. |
If the air cleaner filter is moistened or
polluted excessively or a non-genuine part is used, intake air to
the turbocharger reduces and the pressure in front of turbocharger
drops. So it may cause damage of the turbocharger and oil leaks. .
If the air cleaner filter is moistened or
polluted excessively, replace it with a new one.
|
Replace the air cleaner filter according
to the maintenance
schedule. | |
| 4. |
Check the intercooler hoses &
pipes.
| A. |
Check if the intercooler hoses &
pipes are connected properly. |
| B. |
Check if the intercooler hoses &
pipes are damaged (bent, detached or
torn). |
| C. |
Check if there is any damage, such as
crack, on the intercooler
pipes. |
| D. |
Check if the clamps are positioned in
place. |
If the intercooler hoses & pipes are
damaged or disconnected, oil leaks may occur from the hoses &
pipes and the turbocharger may exceed the permissible speed then it
may cause damage of the turbocharger.
If the intercooler hoses & pipes are
damaged, replace them with new ones.
|
Use new clamps when replacing the hoses
&
pipes. | |
| 5. |
Check the intercooler.
| A. |
Check if the intercooler tubes and tanks
are damaged (oil leak or
crack). |
If the intercooler is damaged, the
turbocharger may exceed the permissible speed then it may cause
damage of the turbocharger.
If the intercooler is damaged, replace them
with a new one.
|
Use new clamps when replacing the
intercooler. | |
| 6. |
Check the engine oil.
| A. |
Check the engine oil
level. |
| B. |
Check the engine oil for discoloration,
water influx and viscosity
degradation. |
| C. |
Check the engine oil
grade. |
If the engine oil level is low, amount of
engine oil fed to turbocharger reduces then the bearings in the
turbocharger may adhere due to insufficient lubrication and cooling.
If the cause of the problem is detected, add
or change engine oil.
|
Change the engine oil according to the
maintenance
schedule. | |
| 7. |
Check the engine oil pressure.
| A. |
Engine oil pressure: Check the oil
pressure using an oil pressure gauge after removing the oil
pressure switch on the cylinder
block. |
| B. |
Check the engine oil screen in the oil
pan if the engine oil level is low. Then check the injectors
for gas leaks if foreign substances are accumulated on the oil
screen. |
If the engine oil level is low, amount of
engine oil fed to turbocharger reduces then the bearings in the
turbocharger may adhere due to insufficient lubrication and cooling.
If the cause of the problem is detected, add
or change engine oil. If foreign substances are accumulated on the
oil screen, wash the oil screen and replace the injector’s washer
with a new one after checking the injectors for gas leaks. Check the
engine oil-related parts, such as oil pump, if
necessary.
|
As the turbocharger rotates at high
speed of 100,000 rpm or above, deterioration of engine oil can
cause damage of the turbocharger bearings. Check engine oil
for discoloration, water influx, viscosity degradation and oil
pressure lowering.
| |
| 8. |
Check the solenoid valve of turbocharger.
(Refer to DTC guide)
| A. |
Damage of the solenoid valve: Check if
vacuum is generated at the disconnected vacuum hose from the
actuator when a forced actuator operating mode is performed by
GDS.. |
| B. |
Clog of the solenoid valve filter: Check
if vacuum is released when a forced actuator operating mode is
performed from max. duty (95%) to min. duty (5%) by GDS. (If
the solenoid valve filter is clogged, the vacuum won’t be
released or it will take a long time to be
released.)
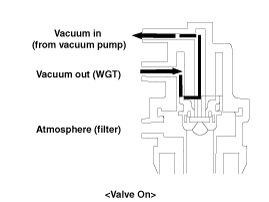
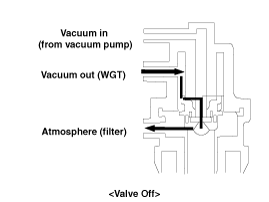
|
If the solenoid valve is damaged, the actuator
does not work properly then it may cause lack of engine power and
poor acceleration. If the solenoid valve filter is clogged, vacuum
is not released then it may cause damage of the turbocharger by
overrunning.
If the solenoid valve is damaged, replace it
with a new one. |
| 9. |
Check the injectors, sensors, EGR valve, etc.
(Refer to FL group)
| A. |
Check if the injectors operate
properly. |
| B. |
Check if the sensors, such as the mass
air flow sensor (MAFS), intake air temperature sensor (IATS),
boost pressure sensor (BPS), operate
properly. |
| C. |
Check if the exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR) valve operates properly.
|
If the injectors, sensors, EGR valve and etc.
don’t work properly, it may cause lack of engine power.
If the cause of the problem is detected,
replace the related parts with new
ones. | |